AI-Powered Use Cases In Utility Transformation And Grid Modernization
By Satish Saini, HEXstream utilities industry specialist
In the first installment of this series, we discussed that among the latest innovations, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and its applications are rapidly increasing in supporting operations and management of the energy & power system. AI-powered algorithms and machine learning (ML) models are more and more innovated, customized and advanced to be widely used in current utility transformation and grid modernization efforts.
In this segment, some specific use cases of AI-Powered application in utilities using Advanced Metering Infrastructure (AMI) / smart metering data will be discussed.
Utility Supply & Demand, Load Forecasting & Planning, Energy Losses
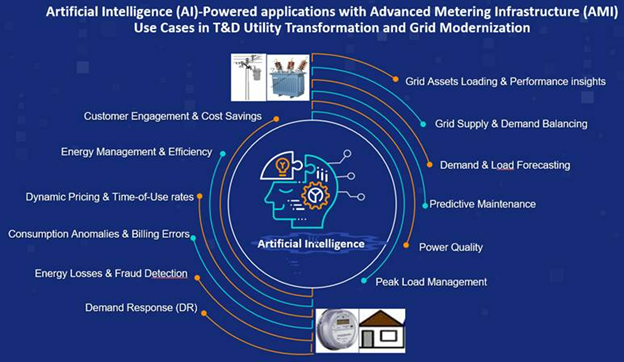
- Utility Demand and Load Forecasting: AI can provide better insights about load and demand patterns across the power grid and help with future demand forecasting by analyzing historical and real time demand and consumption patterns, weather data, and other factors for various communities and segments of the power grid. This can help utilities to better plan their assets upgrades and grid expansions based on forecasted demand.
Use Case:
- Demand and Load Forecasting
- Grid Expansion Planning
- Peak Load Management
- Grid Supply & Demand Balancing - AI can help utilities in balancing supply and demand by analyzing available supply from grid resources and predicting demand and consumption across the grid and help effectively manage energy distribution. This improves the grid’s reliability by reducing the likelihood of blackouts, especially during peak load times. Combining with further utility initiatives and programs on Demand Response (DR) / Demand Side management (DSM), this can be of big relief to utilities when the grid is constrained. Utilities can use AI driven communication to issue alerts to customers on incentives for participating in demand response programs, and subsequently manage demand.
Use Case:
· Supply & Demand Balance
· Demand Response (DR) and Demand Side Management (DSM)
- Energy Losses, Consumption Anomalies, and Fraud Detection- By analyzing smart metering data, AI models can detect unusual patterns or anomalies in energy consumption for specific consumers, communities and grid segments, such as significant spikes or drops in usage. This can help identify potential problems like faulty meters, power theft / pilferage, frauds, or service lines / equipment malfunctions. These AI algorithms on energy losses by spotting suspicious patterns can help prevent revenue losses and ensuring the accuracy of billing by taking corrective actions.
Use Case:
- Frauds & Energy Losses detection
- Faulty Meter Detection
- Consumption Anomalies & Billing Errors
Utility Assets Management and Performance Insights
- Assets Loading: Using and analyzing the historical and real-time AMI data on energy consumption and rolling up to upstream grid assets, AI-powered algorithms can help utilities with meaningful insights on assets loading conditions (like transformers and feeders) and issue alerts on abnormal loading / anomalies. This can help monitor critical assets load and predict future overloading situations, helping utilities take proactive steps in load shifting or assets upgrades.
Use Case:
- Assets Loading Analysis, Overloading alerts, Upgrade Forecasting
- Power Quality: AMI data on power quality parameters like voltage, active and reactive power, power factor, frequency and others can provide useful information and prediction on key operational and performance parameters of critical grid assets. Relevant alerts can be issued triggered by anomalies, significant spikes and dips which can help utilities plan
proactive, preventive and corrective inspections and maintenance activities. This can help prevent significant failures, expensive breakdowns and downtime and saving operational costs
Use Case:
- Assets Power Quality monitoring
- Assets Performance insights
- Assets Predictive & Condition-based Maintenance
Customer Services, Experience and Engagement:
- Enhanced Customer Experience (CX/CIS) with Dynamic Pricing and Energy Efficiency – Using the historical and real-time metering data, AI-driven algorithms can provide energy consumers with insights on their energy usage patterns and can suggest energy-saving tips by adjusting consumption, taking energy efficiency measures and leading to costs savings. This offers a big benefit when the utility has Dynamic Price structure / Time-of-Use rates. Customer can receive alerts from AI driven communication on energy efficiency and incentives for participating in demand response programs as offered by the utility. It can suggest optimal times for high-energy-consuming tasks (like heating or cooling) with minimum applicable rates (wherever applicable).
Use Case:
- Energy Management, Conservation & Efficiency
- Dynamic Pricing, Time-of-Use rates and Load Management
- Consumer Engagement and Energy Management – By analyzing individual customer load and energy consumption data, AI systems can provide personalized feedback and recommendations to customers for efficiently managing energy at their premises. This can be achieved through AI driven alerts and communication on energy usage, saving tips, financial and cost saving benefits and feedback.
Use Case:
- Customer Engagement and Cost savings
- Integration with Building and Home Automation System and IoT Devices - AI can integrate AMI data along with data from IoT (Internet of Things) devices deployed at consumer premises, such as smart appliances, thermostats, and sensors and make relevant and efficient forecasts and predictions. This allows for even greater optimization of energy usage, as AI can control devices in real-time to optimize energy consumption and efficiency.
Use Case:
- AMI Integration with Home Automation and IoT
To conclude, utility AMI data can provide a lot more valuable insights, forecasts and predictions regarding load and demand, assets performance, customer services and energy management. All this can help utilitites toward efficient transformation and grid modernization initiatives.
Up next: We will discuss more about further use cases for T&D utilities in relation to Advanced Distribution Management System (ADMS) towards grid modernization and utility transformation.
